Build a conversational natural language interface for Amazon Athena queries using Amazon Nova | Amazon Web Services
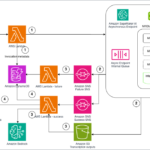
Data analysis often presents significant challenges for business users who aren’t proficient in SQL. Traditional methods require technical expertise to query databases, leading to delayed insights and dependence on data teams. Many organizations struggle with making their data accessible to business users while maintaining the analytical capabilities of Amazon Athena.Continue Reading